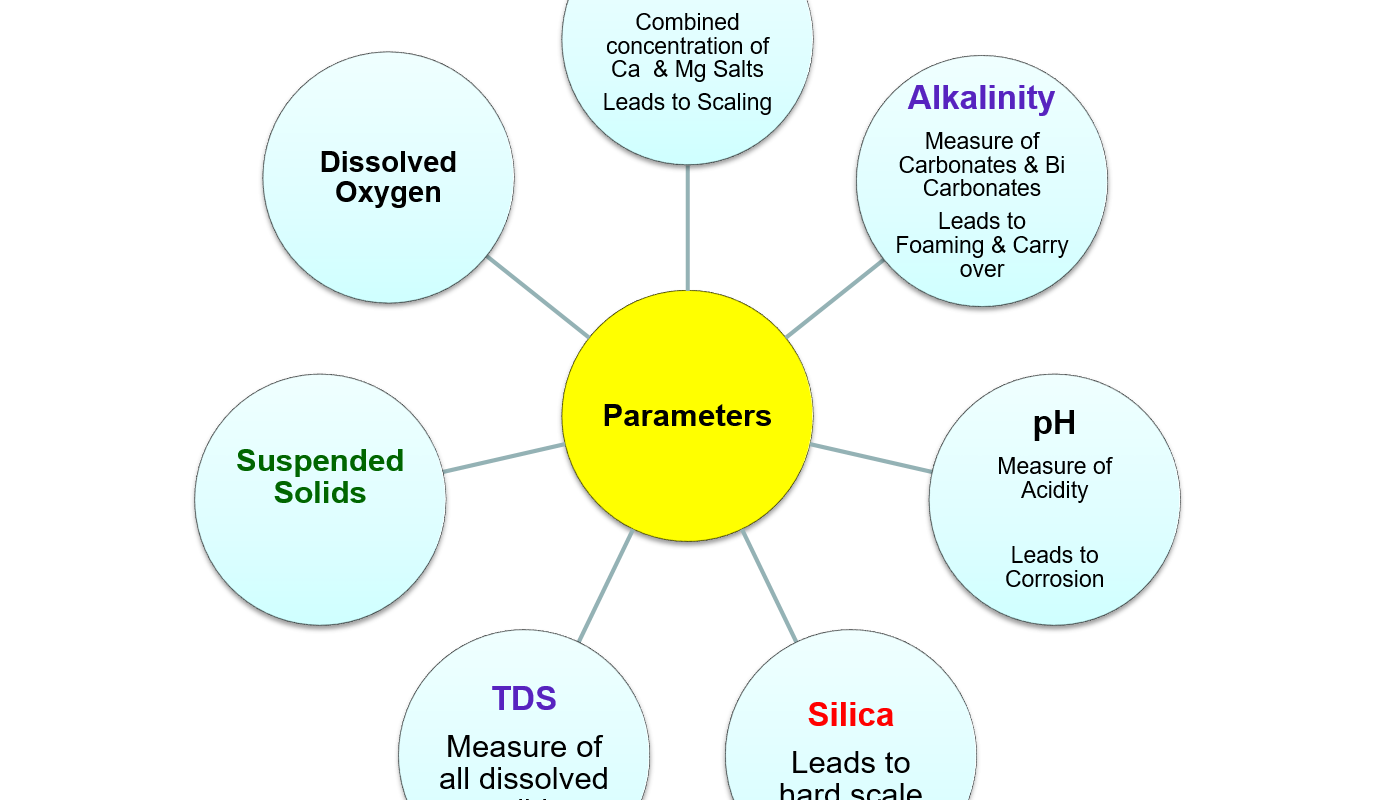
Important water parameters
1.Hardness
2.Alkalinity
3.pH
4.TDS
5.Silica
6.Suspended solids
7.Dissolved oxygen
If there is a difference exists between operating value and target value, then decreasing or increasing blow down and adjusting chemical dosages will be done.
1. Hardness
- Total hardness is the combined concentration of dissolved calcium and magnesium salts.
- Alkaline or temporary hardness is caused by bicarbonates, carbonates or hydroxides. Bicarbonates which predominate in most natural waters are easily broken down when the temperature is raised.
- Non-alkaline or permanent hardness is caused mainly by chlorides, sulphates and nitrates.
- Water hardness is the most common contributor to boiler scaling
Water Hardness classification
- Seawater has a hardness level of 500 mg L-1.
2. Alkalinity
- The extent to which a solution is alkaline (i.e. has a pH value greater than 7)
- It is a measure of its hydroxide (caustic), carbonate and bicarbonate and hydroxides content. Expressed in terms of calcium carbonate content.
- High Alkalinity also contributes to foaming and carryover in boilers.
3. pH
- is a measure of a solution’s acidity
- In water, small numbers of water molecules (H2O) will break apart or disassociate into hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
- Other compounds entering the water may react with these, leaving an imbalance in the numbers of hydrogen and hydroxide ions.
- When more hydrogen ions react, more hydroxide ions are left in solution and the water is basic; when more hydroxide ions react, more hydrogen ions are left and the water is acidic.
Measure of pH
- pH is measured on a logarithmic scale between 1 and 14 with 1 being extremely acid, 7 neutral, and 14 extremely basic. The more extreme the pH, the more likely corrosion problems are to occur
- Because it is a logarithmic scale there is a ten fold increase in acidity for a change of one unit of pH, e.g. 5 is 100 times more acid than 7 on the pH scale
pH = – log [H+] = – log [1 x 10-7] = -[-7] = 7
4. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
- The total dissolved solids (TDS) in water consist of inorganic salts and dissolved materials.
- In natural waters, salts are chemical compounds comprised of
–Anions such as carbonates, chlorides, sulphates, and nitrates (primarily in ground water), and
–Cations such as potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), and sodium (Na).
Measure of TDS
- It is a measure of the total amount of solids in solution. Expressed as parts per million (ppm).
- Generally estimated on-site by measuring electrical conductivity..
- If the design values for TDS are exceeded, carry-over from the boiler will increase leading to a bad steam quality.
WATER QUALITY REQUIREMENT
Drum Water Quality:
- Ph – 9.5 – 10.2
- Total Hardness – Nil
- Total dissolved solids – 100 ppm (Max.)
- Silica as SiO2 – 3 – 5 ppm
- Free Residual Phosphate – 15 ppm
- Dissolved Oxygen – Nil
- Specific elect conductivity at – 200 uS/cm (Max) 25 deg C after degassing
Boiler Feed Water Quality:
- Ph – 8.5 – 9.2
- TSS – Nil
- Suspended matter – Nil
- Total Hardness – Nil
- Total dissolved solids – 0.1 ppm
- Silica – 0.02 ppm
- Specific elect conductivity at – 0.2 uS/cm (Max) 25 deg C after degassing
5. Silica
- Silica is found as dissolved silicate and in a suspended complex form.
- It can combine with other compounds to give scales that are strongly insulating and difficult to remove and cause high resistance to heat transfer
6. Suspended solids (SS)/ Turbidity
- Turbidity is the amount of particulate matter that is suspended in water.
- Nephelometric Turbidity Units
Turbid include: clay ,silt ,finely divided organic and inorganic matter ,soluble organic compounds & organisms. Removed by, coagulation , sedimentation and filtration.
7. Dissolved gases
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide are the most important.
- Dissolved oxygen (DO) is an important factor in determining the corrosiveness of water.
- The solubility of oxygen in water depends on temperature and pressure.
- Dissolved carbon dioxide gives carbonic acid. Even this weak acid can lower the pH to values where the water becomes highly corrosive.