Steam distribution system Components
Most important components
1.Pipes
2.Drain points
3.Branch lines
4.Strainers
5.Filters
6.Separators
7.Steam traps
8.Air vents
9.Condensate recovery system
10.Insulation
1.Pipes
- Pipe material: carbon steel or copper
- Correct pipeline sizing is important
- Oversized pipework:
- Higher material and installation costs
- Increased condensate formation
- Undersized pipework:
- Lower pressure at point of use
- Risk of steam starvation
- Risk of erosion, water hammer and noise
- Size calculation: pressure drop or velocity
- Pipeline layout: 1 m fall for every 100 m
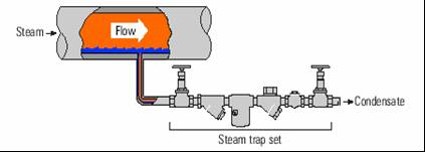
- Drain points
- Ensures that condensate can reach steam trap
- Consideration must be give to
- Design
- Location
- Distance between drain points
- Condensate in steam main at shutdown
- Diameter of drain pipe
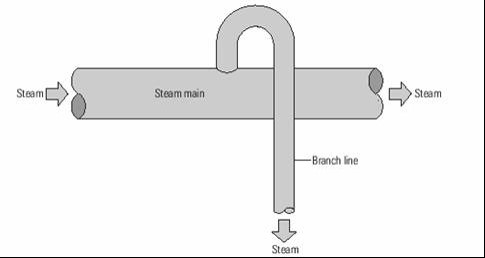
- Branch lines
- Take steam away from steam main
- Shorter than steam mains
- Pressure drop no problem if branch line < 10 m
Branch line connections
- Top: driest steam
- Side or bottom: accept condensate and debris
- Drop leg: low point in branch line
- Sometime steam runs across rising ground
- Condensate should run against steam flow