Steam distribution system components
- Steam traps
- What is a steam trap?
- “Purges” condensate out of the steam system
- Allows steam to reach destination as dry as possible
- Steam traps must handle variations in
- Quantity of condensate
- Condensate temperature
- Pressure (vacuum to > 100 bar)
Selection depends on steam trap’s ability to
- Vent air at start-up
- Remove condensate but not steam
- Maximize plant performance: dry steam
Steam traps – considerations
Water hammer
- Condensate picked up by moving steam
- Can damage steam trap
- Continuous slope in flow direction reduces this
Dirt
- Affects steam trap performance
Strainers
- Help remove dirt and cheaper than maintaining steam traps
Steam locking
- Can occur in rotating machinery
- Only float trap has ‘steam lock release’ valve
Diffusers
- Installed to end of the pipe
- Reduces sound and ferocity of flash steam discharge
Pipe sizing
- Correct pipe size – traps affected by resistance to flow
- Avoid pipe fittings close to trap – back pressure risk
Air venting
- Important for system warm up and operation
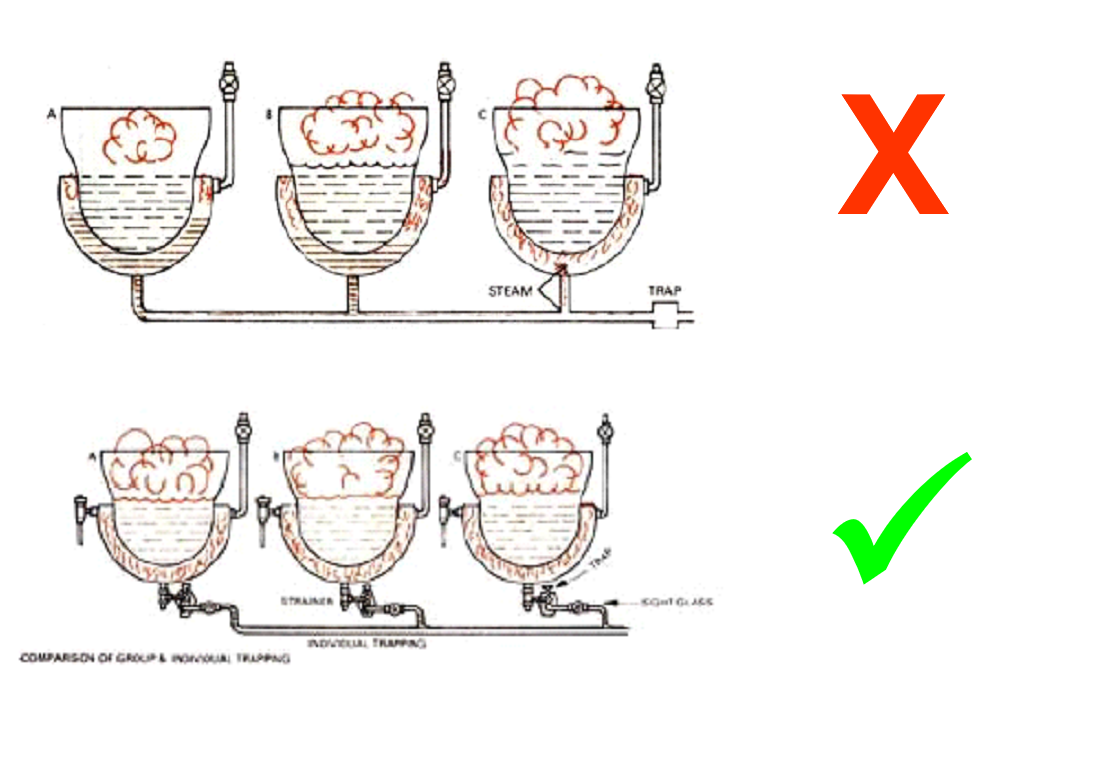
Group trapping
Drain pocket dimensions