Boiler Metallurgy
Requirements of Materials
The following major properties of materials is of interest in the choice of materials for Boiler and Pressure Vessel applications:
- Strength at room temperature and elevated/ service temperature
- Corrosion/ Oxidation resistance
- Stability of structure over a service period normally about 30 years
- Ease of fabrication including welding
Effect of Common Alloying Elements
Carbon: This is the main element which provides strength. For considerations of weldability the carbon content is restricted to 0.25% in IBR and in many of the European codes.
American Code (ASME B&PV) allows carbon up to 0.35%.
The purchase specifications of BHEL restricts the carbon to a maximum value of 0.30%.
Carbon has a major bearing on the high temperature strength also, for example a minimum of 0.04% of carbon is required as per ASME B&PV code to ensure the high temperature creep properties of austenitic SS grades.
Chromium: This is the major alloying element conferring the oxidation /corrosion resistance to the steel. This element also provides resistance to corrosion in sulphur rich flue gases.
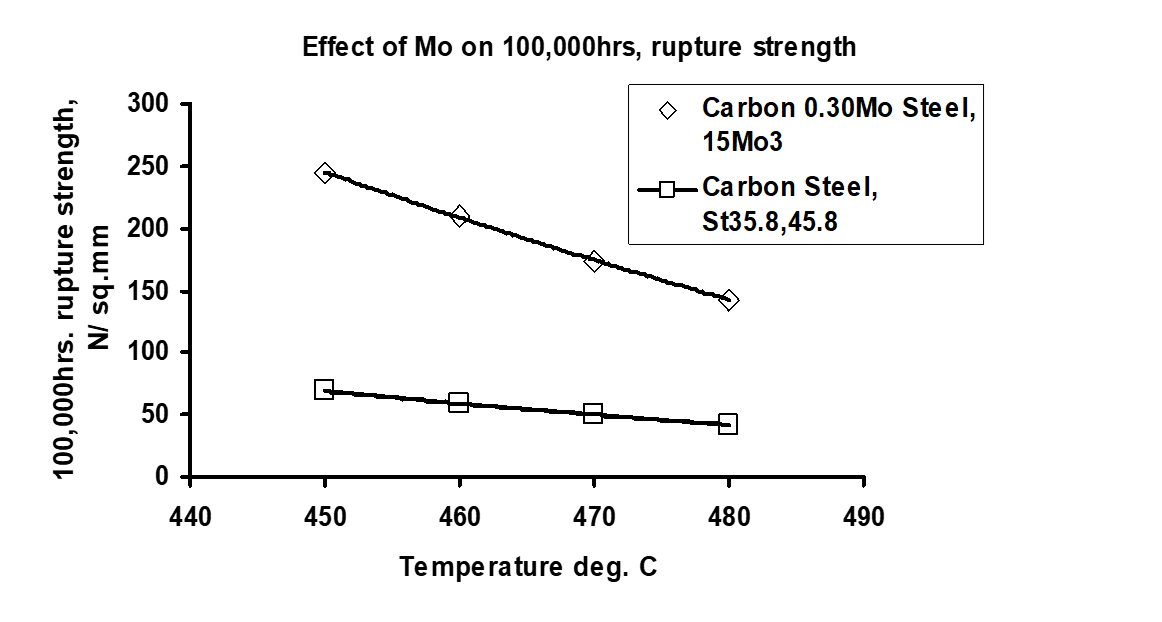
Molybdenum: The main alloy element which confers creep resistance for the steel. 100,000 hrs rupture strength is used in these presentations for the purpose of various comparisons.
Material Selection
- Materials for Main Feed Water Piping : SA 106- C (Carbon Steel)
- Material for Economizer Tubing : SA 210- C (Carbon Steel)
- Material for Water wall Tubing : SA 213- T 22 (2.25 Cr–1.0 Mo)
- Materials for Super heater and Re-heater Tubing : SA 213- T 91 (9Cr-Mo-V)
- Materials for Super heater and Re-heater Steam Piping : SA 335- P 91 (9Cr-1Mo-V)