Soot Blower
1.) What is Soot ?
Soot is a general term that refers to impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolyzed fuel particles such as coal, charred wood, petroleum coke etc.
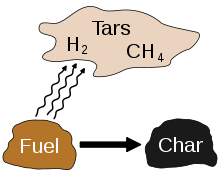
Simplified depiction of pyrolysis chemistry.
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures without the participation of oxygen. It involves the simultaneous change of chemical composition and physical phase, and is irreversible. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements pyro “fire” and lysis “separating.
2.) Why Soot Blower?
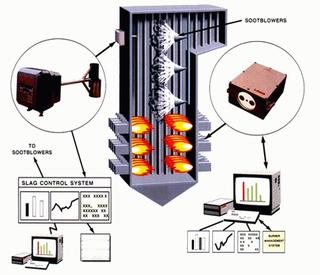
A soot blower is a system for removing the soot that is deposited on the furnace tubes of a boiler during combustion.
Reduced efficiency:
Soot deposited on the heating surfaces of a boiler acts as a heat insulator. The result is that less heat is transferred to the water to raise temp. of steam and more heat is wasted up the chimney. This leads to higher fuel consumption and/or poor steaming.
Soot fires:
A soot fire can be damaging to a boiler because it can cause localized hotspots to occur in the tubes. These hotspots may reach temperatures that weaken the materials of the tubes. Soot blowers reduce the risk of soot fires and their resulting damage.
3.) What is Soot Blower?
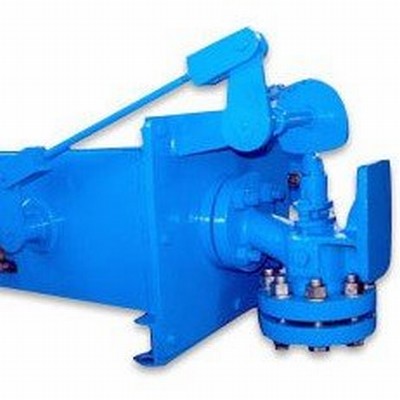
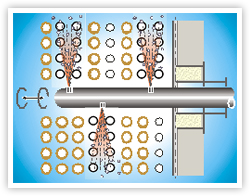
Soot Blower is a mechanism consisting of Soot Blower head mounting box, element & intermediate or end supports. Soot Blowers head is a simple gear train which rotates the spindle and in turn element. The function of Soot Blowers is to keep the Boiler clean & are not expected to remove slag and old deposits. Steam passes through the head and element throughout nozzles, cleaning the loose soot deposited on Boiler Tubes and Super Heater coils and Economizer.
4.) Types of Soot Blower
(1) ROTARY SOOT BLOWERS :
A] LOOSE VALVE TYPE ( NON-IBR)
B] BUILT IN VALVE TYPE – (I) MANUAL & (II) MOTORISED
(2) RETRACTABLE SOOT BLOWERS :
A] SHORT RETRACTABLE –(I) MANUAL & (II) MOTORISED
B] LONG RETRACTABLE –(I) MOTORISED
5.) Working Principle of Soot Blower
The Lance element travels the desired length with steam blowing and again retracts back in anticlockwise direction of rotation with Steam blowing. Travel length is controlled by two heavy duty limit switch.
The Blowing processes begins with the poppet valve actuation as soon as the nozzles passes through the boiler wall.
It is required superheated/saturated steam with desired pressure to clean entire area in high temperature zone. Combination of water with other media such as steam or air have also proven effective but can cause boiler tube damage. Superheated steam is generally recommended over saturated steam to avoid condensation in the cleaning flow, which can accelerate boiler tube erosion or result in thermal cracking.
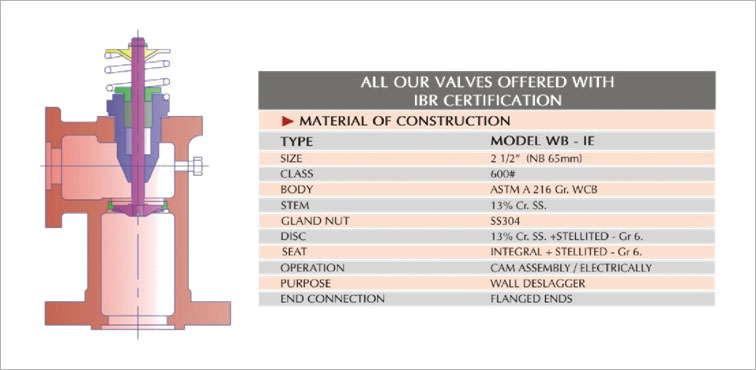
6.) MATERIAL OF CONSTRUCTION
| BLOWING ELEMENT | AISI 304 |
| VALVE BODY | WCB |
| FEED TUBE | SS 304 |
| SOOT BLOWER VALVE | SS 304 |
| CARRIAGE | C.S |
| DISC | SS 304 |
Poppet Valve working:
7.) FREQUENCY OF OPERATION :
The interval between soot blowing periods should be determined by observation under service condition. As a guide line the boiler should be cleaned,
- a) Shortly after start up when full W.P. obtained.
- b) Approximately every eight-hour service.
8.) PRECAUTIONS DURING OPERATION:
* The boiler should be on @ 75% load when soot blowing to ensure that increased gas velocity through the boiler which helps to carry away the loosened deposits originating from the soot blowing.
* Do not start two soot blowers at a time.
* Never run a soot blower without steam when boiler is running.
* Normal sequence of soot blowing is to follow the gas flow through the boiler.