HVAC
What is HVAC?
- Heating, Ventilation, Air conditioning
- Controls temperature, humidity and air quality inside a building
- Especially important in medium to large buildings such as office/residential towers
- All preferably integrated into one system
- In warm climates usually no need for a heating system
1.) Heating:-
- Central heating often used in cold climates to heat private houses and public buildings.
- Heating systems usually comprise of a boiler, furnace, heat pump or district hot water to heat water, steam or air.
- Piping distributes heated fluid and radiators transfer this heat to air and structures, e.g. floor heating system.
2.) Ventilation:-
- The process of ”changing” or replacing air in any space to control temperature or remove moisture, smoke, carbon dioxide, etc
- Ventilation includes both the exchange of air to the outside as well as circulation of air within the building.
- One of the most important factors for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality in buildings.
- Supply air used for ventilation is filtered and cooled and/or heated inside air handling units.
3.) Air conditioning:-
- Refers to the cooling and dehumidification of indoor air for thermal comfort.
- Air conditioning systems are designed to stabilize the air temperature and humidity within an area.
- Excess heat from the circulating air is usually removed by a cooling coil that is supplied with cold water.
- To decrease relative humidity the circulating air needs to be cooled to a temperature below the dew point and then heated back to meet the requirement.
Major terms of HVAC
- Air handling unit (AHU) – a central unit consisting of a blower, heating and cooling elements, filters, etc. that are in direct contact with the airflow.
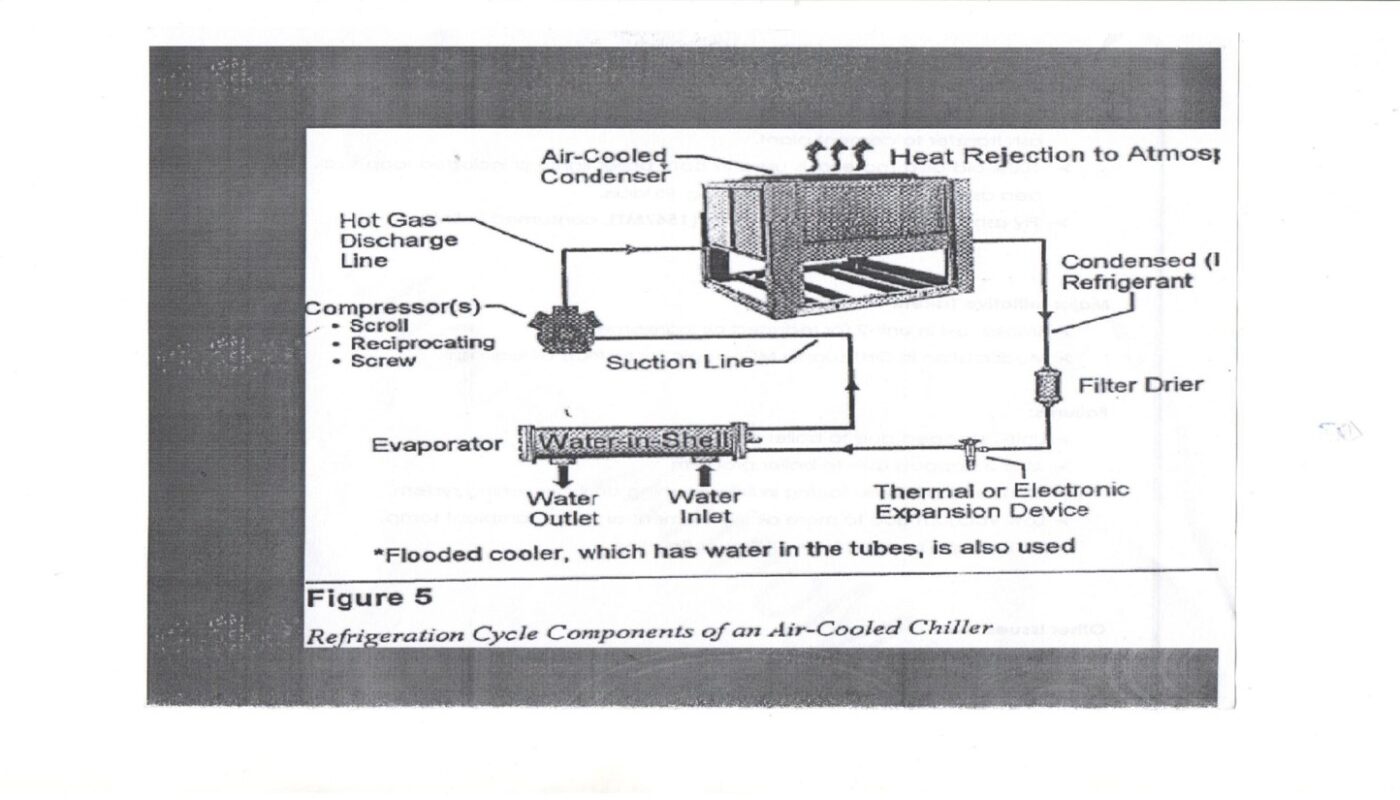
- Chiller – a device that removes heat from a liquid .The cooled liquid flows through pipes and passes through coils in air handling units, FCUs, etc
- Coil – equipment that performs heat transfer inside an AHU etc.
- Damper – a plate or gate placed in a duct to control airflow.
HVAC Components
HVAC operation and trouble shooting
1.) Low Suction Pressure:-
BELOW 10 PSI
- Check suction water pressure. It should be above parameter
- Check parameters setting Gas pressure- Static- 90-110 PSI Running- 25-30 PSI
- Check sensor feedback. It should between 4 to 20 mA.
- Expansion valve to be check working or not 1) Direct supply and battery supply to be healthy -11-18V.
2.) High Discharge Pressure:-
ABOVE 260PSI
- Condensate fan to be check running or not (relay to be check)
- Check discharge pressure. It should be lower then parameter setting
- Fin cleaning to be done
- Parameters to be check
- Sensor to be check (suction and dis.)
- Check sensor feedback. It should between 4 to 30 mA.
- Check polarity it should be as per sensor drawing
3.) Zone -B:-
75% and above 240 PSI for 1 min.
- Condensate fin to be check for cleaning
- Refrigerant pr. To be check according to ambient Static- 90-110 PSI Running – 25-30 PSI
- Expansion valve to be check working or not 1) Direct supply and battery supply to be healthy -11-18V.
4.) Zone -F:-
100% load for 1 min.
- Condensate fin to be check for cleaning
- Refrigerant pr. To be check according to ambient Static- 90-110 PSI Running – 25-30 PSI
- Expansion valve to be check working or not 1) Direct supply and battery supply to be healthy -11-18V.